Para realizar el proyecto, uno de los pasos importantes es verificar que nuestro sistema tenga estabilidad y para ello una manera de ver e identificar que nuestro sistema es realmente estable se pueden realizar distintos diagramas tales como diagrama de bode, respuesta y nyquist.
Primero veremos algo del código del cual es relativamente corto, con la ayuda de la librería de control se usaron las funciones para dibujar y representar la función de transferencia.
Recordando que nuestra función de transferencia es la siguiente:
Ahora veamos los diagramas que nos dio nuestro programa.
Diagrama de bode:
Diagrama de respuesta:
Diagrama de nyquist:
Conclusión
Tomando en cuenta la teoría de las definiciones del libro de control que se lleva en la materia, se puede decir que nuestro sistema es estable debido a que cumple con las siguientes características nuestro sistema en los diagramas anteriores, cumplen con un ligero cambio y no sufre de cambios bruscos, ademas los diagramas de respuesta cumplen con lo deseado, ya que la respuesta que se espera es ligero y no brusco. Basandome en una presentación donde muestra un sistema parecido me di cuenta que nuestro sistema cumple con algunas características típicas cuando se hace control de un motor dc.
martes, 30 de octubre de 2012
Sistema de Transiciones: Elevador
A continuación veremos mi sistema de transiciones que consiste en un elevador y una puerta, basandome en la entrada anterior en donde modele el mismo sistema hice el sistema de transiciones en donde también se corrigieron unos errores cometidos en el modelo de la red petri en donde nunca regresaba a un estado inicial.
Y este es el código que hice en promela basandome en la explicación de las diapositivas que dejaré debajo.
Fuente:
Diapositivas de promela.
Y este es el código que hice en promela basandome en la explicación de las diapositivas que dejaré debajo.
Fuente:
Diapositivas de promela.
domingo, 28 de octubre de 2012
Steganography Assignment
Here's my code in three of the six photos. I recommend to download these photos from the link below because blogspot changes something and it's difficult to recover the information.
After the deadline, I'm going to explain how my algorithm works.
Parameters to encrypt:
1.- Name of the text to encrypt
2.- The image to hide the message
3.- The name of the image with the message
Example:
imagenes.py photo8.bmp copia8.bmp
Parameters to decrypt:
1.- Name of the image with the message
2.- The file to put the message
3.- The keyword "decripta"
Example:
copia6.bmp recuperado6.dat decripta
Código
**Note** The three images with message are the number 1, 3 and 5.
jueves, 25 de octubre de 2012
Stream ciphers: Trivium
What is Trivium?
Trivium is a hardware oriented synchronous stream cipher, that was designed as an exercise in exploring how far a stream cipher can be simplified without sacrificing its security, speed or flexibility.
Trivium is a synchronous stream cipher designed to generate up to 2 ^64 bits of key stream from an 80-bit secret key and an 80-bit initial value (IV), the process consists of two phases: first the interntal state of the cipher is initialized using the key and the IV, then the state is repeatedly updated and used to generate key stream bits. These are the parameters:
Key size: 80 bit
IV size: 80 bit
Internal state: 288 bit
Who invented Trivium?
It was submitted to a eSTREAM competition by its authors, Christophe De Cannière and Bart Preneel, and has been selected as part of the portfolio for low area hardware ciphers by the eSTREAM project, It's not patented.
How does It work?
Key stream generation; The proposed design contains a 288-bit internal state denoted by (s 1, ..., s 288). The key stream generation consists of an iterative process which extracts the values of 15 specific state bits and uses them both to update 3 bits of the state and to compute 1 bit of key stream z i. The state bits are then rotated and the process repeats itself until the requested N <= 2 ^64 bits of keys stream have been generated. Here is a pseudo-code:
Where "+" and "." operations stand for addition and multiplication over GF(2), which is the Galois Field of two elements (XOR and AND).
Key and IV setup; the algorithm is initialized by loading an 80-bit key and an 80-bit IV into the 288-bit initial state, and setting all remaining bits to 0, except for s ^286, s ^287 and 2 ^288, then the state is rotated over 4 full cycles without generating key stream bits.
Key and IV setup; the algorithm is initialized by loading an 80-bit key and an 80-bit IV into the 288-bit initial state, and setting all remaining bits to 0, except for s ^286, s ^287 and 2 ^288, then the state is rotated over 4 full cycles without generating key stream bits.
Attacks known
There are some attacks known as you can see below:
Source:
Article where you can see specifications.
Article Algebraic Attack
http://www-polsys.lip6.fr/~jcf/Papers/SCC08c.pdf
Two Trivial Attacks on Trivium
https://www.cosic.esat.kuleuven.be/ecrypt/stream/papersdir/2007/006.pdf
Cube Attacks on Trivium
http://eprint.iacr.org/2009/015.pdf
Suscribirse a:
Entradas (Atom)

























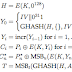
;04014806.jpg)