- Hacer detección de borde.
- Elegir pares antiparalelos.
- Generar votos a tomando como frontera el borde y las rectas de pares antiparalelos.
- Determinar a partir de porcentaje de votos sí realmente es un elipse (Por agregar).
Lo primero es necesario para saber en que area vamos a trabajar, después de saber el area en la que trabajamos, se empiezan a tomar pares de puntos aleatorios para luego sacar su punto medio y tomarlo como voto. A partir del porcentaje de votos se podrá determinar sí es un elipse.
Ahora lo que se implementó, tuve grandes problemas donde dichos problemas eran de herencia de tareas anteriores con los indices en donde estaban en algunos invertidos en otros no. En fin lo que se implementaron solamente fue la realización de los votos y la creación de las rectas antiparalelas con puntos aleatorios seleccionados. Esto fue lo que obtuve.










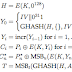

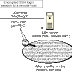


Viendo tus rectas es obvio que algo aritmético va mal. Mejor dibuja el segmento para un sólo par de puntos para ver qué está mal (orientación, selección del par, algo de índices, etc.) 3 pts.
ResponderEliminarNP tarea 6.
ResponderEliminar