Se realizaron pruebas por medio del código presentado en clase en donde detectaba líneas. Lo que presentaré a continuación es simplemente clasificación de líneas y una liviana detección de líneas diagonales. Primero veremos las imágenes filtradas.
Laberinto.
Cuadrado.
Gráficas.
Ahora diferentes figuras geometrícas. Y bueno tuve unos problemas, al momento de detectar las líneas diagonales algunas pueden ser detectadas y otras no, como pueden observar abajo.
Ahora veamos el siguiente código el cual ya lo había presentado y solamente agrege una función de math llamada degree en python, para obtener el ángulo en el plano del arco tangente. Código:
Suscribirse a:
Enviar comentarios (Atom)












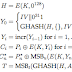



Pues, batalla con algunas orientaciones, pero es un avance bastante notable. 5 pts.
ResponderEliminar