method to compress the image. Huffman is a method that makes a three
keywords where each keyword has a value that have less weight than the
one that is replaced, and as you get more large the three the high
frequencies are more weight than the ones with high frequencies.
Below we can see an example of how does it work.

In the program that I made you need to put a keyword "comprimir" to
select that you wanna compress a file or "descomprimir" to select that
you wanna descompress a file, after you press enter you are gonna put
you're file name once that you put it, the compression or
decompression begins.

When you compress a file with my program you are gonna see in the
terminal a dictionary of frequencies of the values followed by a
binary file created with the Huffman's algorithm and then the time
of execution.
The flow for compress is the next one:

And the flow for decompress is the follow one:

All this happen using the pixel value of each coordinate of the image,
and then using the flow that I mencioned before we can get the image
compressed or decompress (once is compressed).
A good way to examine the performance is saving the time of execution
and the size of the file that print out my program. To see how the performance
is going I recommend a linear graph.
The program just is working for compression, I had problems to decompress
the file but the logic pretty much the same as previous programs that I made
about using Huffman's algorithm.
This is the code that I made:










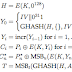


En el reporte hubiera sido bueno incluir algo de ejemplos, pero entiendo que si hay broncas con la decompresión, no es tan fácil. Van 4 pts por el reporte. El código sí es original y comentado, aunque con varios detalles de ortografía. Lástima que no jaló la decompresión. Es posible que tengas mal los índices otra vez. Van 5 pts por el código.
ResponderEliminar