Los satélites hoy en día son usados para:
- Transmitir en ciertas areas TV.
- Para realizar una red de datos corporativos.
- Para realizar una red de telefonía conmutada (ISP).
- Transmitir y recibir internet.
- Distribución de vídeos (cines).
- Realizar comunicación con el ISP (el proveedor de servicio del internet).
Existen 4 tipos de satélite:
- Satélites LEO (Low Earth Orbit, órbita baja) tienen una altitud de 500 - 2,000 km de la Tierra.
- Satélites MEO (Medium Earth Orbit, órbita media) tienen una altitud de 8,000 - 20,000 km de la Tierra.
- Satélites HEO (Highly Elliptical Orbit, órbita elíptica) tienen una altitud menor a los 35,786 km.
- Satélites GO (Geostationary Orbit, órbita geoestacionario), tienen una altitud de 35,786 km.
A continuación veremos una imagen que nos muestra el tipo de órbita que realiza cada uno de los tipos de satélites antes mencionados.
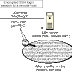
La mayoría de los satélites se componen de la siguiente manera:
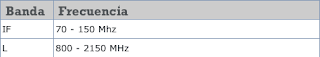
Las frecuencias utilizadas por las antenas son las siguientes:
Estas son las usadas por los satélites.
Las redes VSAT (Very Small Aperture Terminals) son redes privada de comunicación de datos vía satélite para intercambio de información. Se componen por estas características :
- Tienen 2 tipos de comunicación satélital.
- Se usa un pequeño disco como antena (diámetro 75cm - 2,4m).
- Son administrados por el HUB (en este caso desde una estación maestra).
Existen varios tipos de topologías del VSAT, estas son algunas:
- Transmisión simplex. La aplicación que tiene este tipo de topología es la transmisión de difusión como los son la TV y servicios de video así como el servicio de radio.
- Transmisión Duplex de Punto a Punto. La aplicación que tiene este tipo de topología es el transporte de telefonía de voz, datos y IP (especialmente en configuraciones asimétricas), redes corporativas, contribución y distribución de programas de TV.
- Transmisión de un punto a múltiples puntos. La aplicación que tiene este tipo de topología es para la creación de redes corporativas, negocios en servicio de TV, servicios de internet entre otros.
- Servicio de antena móvil. La aplicación que tiene este tipo de topología es para el periodismo electrónico por satélite, para emisión y difusión de eventos especiales, servicios marítimos entre otros.
- Red estrella. La aplicación que tiene este tipo de topología es usado para redes corporativas ó para la enseñanza a distancia.
- Red malla. La aplicación que tiene este tipo de topología es para crear redes de datos y telefonía nacional e internacional.
Existen 3 formas de acceder a ellos:
- FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access, Acceso Múltiple por división de frecuencia) es una técnica de multiplexación en múltiples protocolos de comunicaciones tanto digitales como analógicos, principalmente de radiofrecuencia, y entre ellos en los teléfonos móviles de redes GSM.
-
El acceso al medio se realiza diviendo el espectro disponible en canales, que corresponden a distintos rangos de frecuencia, asignando estos canales a los distintos usuarios y comunicaciones a realizar, sin interferirse entre sí.
- TDMA (Time Division Multiple Acces, Multiplexación por División de Tiempo) es una técnica que permite la transmisión de señales digitales y cuya idea consiste en ocupar un canal de transmisión a partir de distintas fuentes, de esta manera se logra un mejor aprovechamiento del medio de transmisión. TDMA es una técnica de múltiplexación que distribuye las unidades de información en ranuras ("slots") alternas de tiempo, proveyendo acceso múltiple a un reducido número de frecuencias.
- CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access, Multiplexación por División de Código) es un término genérico para varios métodos de multipleación o control de acceso al medio basados en la tecnología de espectro expandido pueden emplearse indistintamente espectro ensanchado, expandido, difuso o disperso.
Los datos a transmitir simplemente se les aplica la función lógica XOR con el código de transmisión, que es único para ese usuario y se emite con un ancho de banda significativamente mayor que los datos.
Como se pudieron percatar los satélites son bien usados para casi las mayorías de las cosas que sucede en el mundo en cuestiones de tecnología y aquí es donde los hackers se involucran más; En la red se confía cierta información como de gobierno, clientes, ventas, multimedia, telefonía, acceso al banco, entre muchos otros, teniendo acceso a esta información se podría causar desde un simple robo hasta ocasionar un posible guerra.
Actualmente existen algunos tipos de ataques de satélite:
Servicio Denegado (DoS).
- Jam Uplink es crear una interferencia en el enlace de subida.
- Overpower Uplink es tener el dominio de un enlace de subida.
- Jam Downlink es crear una interferencia en el enlace de subida.
Posicionamiento Orbital (Orbital Positioning).
- Comando directo (Direct Commanding) es tener un acceso directo al satélite y poder controlar su funcionalidades de orbitación.
Algunos hackers buscan alguna vulnerabilidad en los ATM's que tienen comunicación por satélite.
Actualmente el banco tiene dos problemas el primero es por parte de los usuarios y el segundo el sistema.
Por parte del usuario se tienen los problemas de una contraseña débil, son muy vulnerables al pishing y algunos les falta un poco de habilidades.
Por parte del sistema se tiene problemas porque los sistemas están fuera de tiempo, están configurados de una manera insegura y algunos tienen puertos inseguros o algunos simplemente dejan puertos abiertos.
Otro caso que me pareció muy interesante fue que unos hackers quieren comenzar a poner en órbita satélites para evitar la censura en la internet, esto debido a la propuesta de leyes como SOPA. Aquí les pongo un video sobre el proyecto que proponen y una liga a la noticia.
Noticia.
http://thehackernews.com/2012/01/hackers-launching-own-satellites-in.html
Existe una noticia muy relacionada sobre la censura también pero este va relacionada con la famosa página llamada ThePirateBay, en la cual están planeando tener servidores en las nubes con drones de baja órbita, esto para evitar que sigan operando.
Noticia.
http://thehackernews.com/2012/03/pirate-bay-plans-low-orbit-server.html
Otra noticia interesante es sobre los múltiples hackeos que han realizado los chinos, se dice que estos son realizados por un escuadrón en específico que son entrenados para hacer diversos tipos de hacking. El último hackeo que han hecho ha sido a un satélite de USA y aún se sabe que información fue tomada.
Noticia.
http://thehackernews.com/2011/10/us-satellites-was-victim-by-chinese.html
Entre los temas más predominantes del hacking en los satélites son sobre temas de dinero, censura e información gubernamentales.
Referencias.
Jim Geovedi, Raditya Iryandi, Raoul Chiesa. Hacking a Bird in the Sky
http://www.slideshare.net/geovedi/hacking-a-bird-in-the-sky-the-revenge-of-angry-birds
Satellite frequencies
http://www.inetdaemon.com/tutorials/telecom/satellite/frequencies.shtml
About VSAT Very Small Aperture Terminal
http://vsatcaribbean.com/vsat-satellite-basics-guide.html#About%20VSAT
FDMA
http://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acceso_múltiple_por_división_de_frecuencia
TDMA
http://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acceso_múltiple_por_división_de_tiempo
CDMA
http://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acceso_múltiple_por_división_de_código
ATM photo
http://www.networkinv.com/wp-content/uploads/bgan-atm-630x298.jpg











































;04014806.jpg)